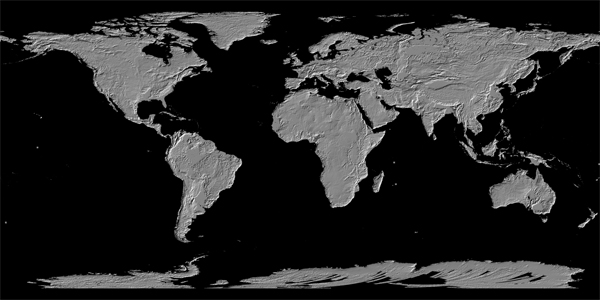
|
| Release of ASTER GDEM Version 3 (06 August, 2019) |
|---|
|
The United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) and the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) of Japan today jointly released Version 3 of the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) The ASTER GDEM is available at no charge to users worldwide via electronic download from Japan Space Systems and from NASA’s Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC). With this release, an additional global product is now available: the ASTER Water Body Dataset (ASTWBD). This raster product identifies all water bodies as either ocean, river, or lake. Each GDEM tile has a corresponding Water Body tile. This data product provides the only water mask covering nearly the entire surface of the earth. Please refet to this pdf in detail. |
| Release of ASTER GDEM Version 2 (03 October, 2011) |
The ASTER Global Digital Elevation Model (ASTER GDEM) is a joint product developed and made available to the public by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) of Japan and the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). ?It is generated from data collected from the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER), a spaceborne earth observing optical instrument. The ASTER GDEM is the only DEM that covers the entire land surface of the Earth at high resolution.? Since the release of the Version 1 on June 29, 2009 (*1), the ASTER GDEM has been widely used by many users (*2) and it has greatly contributed to the global earth observing community. (*1) METI press release (June 26, 2009) Version 2 of the ASTER GDEM is developed, employing an advanced algorithm to improve GDEM resolution and elevation accuracy and reprocessing a total of 1.5 million scene data including additional 250,000 scenes acquired after the previous release.? Accuracy of this latest version is validated by the collaborate effort between Japan and the United States, which shows significant improvements over Version 1 (*3).? The ASTER GDEM Version 2 will be formally released as an upgrade to Version 1 on October 17, 2011. (*3) Link to “Quality Improvements in Version 2” 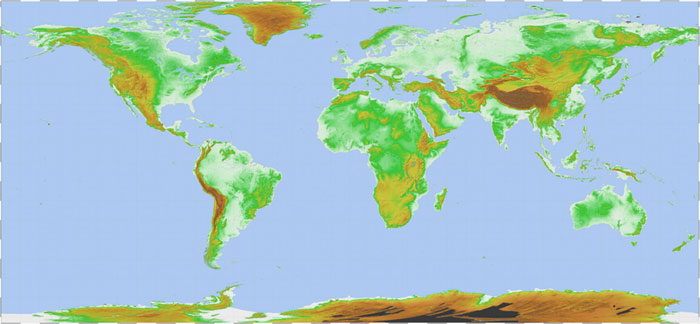 |
| Final Release Announcement (29 June, 2009) |
METI and NASA Release ASTER Global DEM The Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) of Japan and the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) today jointly released Version 1 of the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM). Previously, METI and NASA announced their intent to contribute the ASTER GDEM to the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS). Consequently, the ASTER GDEM is available at no charge to users worldwide via electronic download from the Earth Remote Sensing Data Analysis Center (ERSDAC) of Japan and from NASA’s Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC).
The ASTER instrument was built by METI and launched onboard NASA’s Terra spacecraft in December 1999. It has an along-track stereoscopic capability using its near infrared spectral band and its nadir-viewing and backward-viewing telescopes to acquire stereo image data with a base-to-height ratio of 0.6. The spatial resolution is 15 m in the horizontal plane. One nadir-looking ASTER VNIR scene consists of 4,100 samples by 4,200 lines, corresponding to about 60 km-by-60 km ground area. The methodology used to produce the ASTER GDEM involved automated processing of the entire 1.5-million-scene ASTER archive, including stereo-correlation to produce 1,264,118 individual scene-based ASTER DEMs, cloud masking to remove cloudy pixels, stacking all cloud-screened DEMs, removing residual bad values and outliers, averaging selected data to create final pixel values, and then correcting residual anomalies before partitioning the data into 1°-by-1° tiles. It took approximately one year to complete production of the beta version of the ASTER GDEM using a fully automated approach. The ASTER GDEM covers land surfaces between 83°N and 83°S and is composed of 22,600 1°-by-1° tiles. Tiles that contain at least 0.01% land area are included. The ASTER GDEM is in GeoTIFF format with geographic lat/long coordinates and a 1 arc-second (30 m) grid of elevation postings. It is referenced to the WGS84/EGM96 geoid. Pre-production estimated accuracies for this global product were 20 meters at 95 % confidence for vertical data and 30 meters at 95 % confidence for horizontal data. Initial studies to validate and characterize the ASTER GDEM confirm that pre-production accuracy estimates are generally achieved for most of the global land surface, although results do vary and true accuracies do not meet pre-production estimates for some areas. In addition, Version 1 of the ASTER GDEM does contain certain residual anomalies and artifacts that affect the accuracy of the product and may be impediments to effective utilization for certain applications. Consequently, METI and NASA acknowledge that Version 1 of the ASTER GDEM should be viewed as “experimental” or “research grade.” Nevertheless, they are confident that the ASTER GDEM represents an important contribution to the global earth observation community. ASTER GDEM tiles may be downloaded electronically from ERSDAC by visiting http://www.gdem.aster.ersdac.or.jp/and from the LP DAAC by visiting https://wist.echo.nasa.gov/~wist/api/imswelcome/. |
| Pre-release announcement (Jun.26,2009) |
METI and NASA Announce Plans for ASTER Global DEM Release The Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) Global Digital Elevation Model (GDEM) was developed jointly by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) of Japan and the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). Initial studies to validate and characterize the ASTER GDEM recently were completed by NASA and METI, in cooperation with the U.S Geological Survey (USGS) and the Earth Remote Sensing Data Analysis Center (ERSDAC) of Japan, as well as with support from the U.S. National Geospatial-Intelligence Agency (NGA) and numerous other collaborators from around the world.
Following review of the validation results, METI and NASA have decided to jointly release the ASTER GDEM on June 29, 2009. Previously, METI and NASA announced their intent to contribute the ASTER GDEM to the Global Earth Observation System of Systems (GEOSS). Upon release, the ASTER GDEM will be available at no charge to users worldwide via electronic download from ERSDAC and from NASA’s Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC) by visiting http://www.gdem.aster.ersdac.or.jp/ and https://wist.echo.nasa.gov/~wist/api/imswelcome/, respectively. The ASTER instrument was built by METI and launched onboard NASA’s Terra spacecraft in December 1999. It has an along-track stereoscopic capability using its near infrared spectral band and its nadir-viewing and backward-viewing telescopes to acquire stereo image data with a base-to-height ratio of 0.6. The spatial resolution is 15 m in the horizontal plane. One nadir-looking ASTER VNIR scene consists of 4,100 samples by 4,200 lines, corresponding to about 60 km-by-60 km ground area. The methodology used to produce the ASTER GDEM involved automated processing of the entire 1.5-million-scene ASTER archive, including stereo-correlation to produce 1,264,118 individual scene-based ASTER DEMs, cloud masking to remove cloudy pixels, stacking all cloud-screened DEMs, removing residual bad values and outliers, averaging selected data to create final pixel values, and then correcting residual anomalies before partitioning the data into 1°-by-1° tiles. It took approximately one year to complete production of the beta version of the ASTER GDEM using a fully automated approach. The ASTER GDEM covers land surfaces between 83°N and 83°S and is composed of 22,600 1°-by-1° tiles. Tiles that contain at least 0.01% land area are included. The ASTER GDEM is in GeoTIFF format with geographic lat/long coordinates and a 1 arc-second (30 m) grid of elevation postings. It is referenced to the WGS84/EGM96 geoid. Pre-production estimated accuracies for this global product were 20 meters at 95 % confidence for vertical data and 30 meters at 95 % confidence for horizontal data. Initial validation studies concluded that the ASTER GDEM generally meets the pre-production accuracy predications, but results do vary and include areas where GDEM accuracy does not meet the pre-production estimates. The topography of the land surface is one of the most fundamental geophysical measurements of the Earth, and it is a dominant controlling factor in virtually all physical processes that occur on the land surface. Topography of the land surface also significantly controls processes within the overlying atmosphere, and it reflects the processes within the underlying lithosphere. Consequently, topographic information is important across the full spectrum of earth sciences, and the availability of an up-to-date, high resolution (1-arc-sec or less) global DEM has been a priority of earth scientists for a long time. The ASTER GDEM, with 30m grid postings and produced from a consistent primary data source, is expected to meet the requirements of many users for global topographic information. |